20 Ways to Manage Herbicide Residues | 16th is the Best!
It is the need of today to manage herbicide residue in soil and plants. This carryover may be buildup and may enter the food chain. Following practices can limit the adverse effects of herbicidal residues;
20 Ways to Manage Herbicide Residues
Following practices can limit the effect of herbicidal residues on soil, plants, and animals.
- Using an optimum dose of herbicides can be effective. It is better to consider the lowest possible dose to achieve desired weed control and manage herbicide residues.
- Band application of herbicide in line, ridge, and bed sown crops (cotton, sorghum, maize, sugarcane) is more desired rather than broadcast application. By applying herbicides in bands, one can limit the amount of herbicide applied.

- The application of farmyard manure (FYM) is effective as a colloidal fraction of FYM may absorb herbicide molecules and manage herbicide residue.
- FYM also enhances microbial activity to degrade herbicidal residues frequently.
- The deep manipulation of the soil with a disc plow or other secondary/tertiary tillage implements can mix the available residues with a greater volume of soil and dilute it.
- Using a moldboard plow (MB Plough)to manage herbicide residue is a well-known practice. It can invert the soil with residues in deeper layers thus reducing soil toxicity.
- Crops with intensive use of herbicide should be rotated with crops requiring less herbicide treatment. E.g. Ragi – cotton – sorghum.
- Growing tolerant crops in the successive growing season will perform well in soil with carry-over herbicide residues. A tolerant crop can degrade or store herbicide to a non-toxic compound and thus can manage herbicide residue in soil and plant.
- Along with crop rotation, herbicide formulation should also be rotated. This is required otherwise weeds may develop resistance to a particular herbicide being used for years.
- The dose of herbicide should be as accurate as recommended to avoid the carry-over effects of residues. If there is a good percentage of organic matter content, then it is better to use a lower dose of Trifluralin on the sandy soils.
- Application time of herbicides also matters. Pre-emergence and early application result in minimum chances of residual carry-over chances for the next season. Early applied herbicides face degradation factors like moisture, temperature, and light for a longer time.
- Careful application and proper calibration of herbicide are also essential to reduce potential carryover. Always ensure to apply uniform boom, and avoid overlapping and sharp turns in the field.
- Manual or mechanical weeding in the case of row plantations can limit the input of herbicide in the soil.
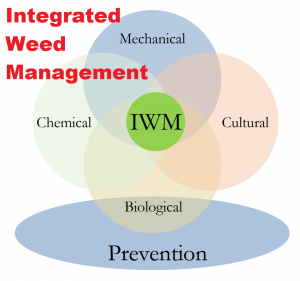
- Integrated weed management may provide better results. By using manual, mechanical, cultural, and biological means of weed control, one may limit the addition of herbicide to soil and crop. Cultural techniques like fertilizer placement, crop selection, and sowing time also minimize the level of residual carryover.
- The addition of fertilizer Enhances crop growth and thus uptake of the herbicide from the soil. It also enhances the growth of microflora and the biological degradation of herbicide. Biological degradation is generally by oxidative processes e.g. beta-oxidation, N-oxidation, N-demethylation, C-hydroxylation, C-cleavage, C-reduction, and hydrolysis. The addition of Phosphorous accelerates microbial degradation of phenoxy herbicide (MCPA)
- Adding adjuvants e.g. non-phytotoxic oil in atrazine serves a dual purpose. It enhances the weed-killing potency of atrazine and reduces residual hazards as well.
- Activated carbon (charcoal) has high absorptive capacity due to greater surface area. It can absorb residues without affecting crop yield.
- Safeners and antidotes induce the activity of herbicide detoxifying enzymes. These protect crop plants from possible herbicide damage. NA (1,8 Naphthalic Anhydride) is used as a seed dressing in rice and Cyometrinil is used as a safener in grain sorghum.
- Addition of Charcoal increases the Adsorption of herbicides. Though, the use of charcoal on large scale is not feasible economically. However, we can only use charcoal as Spot treatment or on the areas of high-value crops (Horticultural Crops)
- Frequent irrigation can limit the residual effect of water-soluble herbicides in no time. Herbicides leached down to deeper layers, beyond the crop rhizosphere.
If you are more concerned about the analysis of herbicide residues, read the article, Determination of herbicide Residues
Alerts
The application of Farm Yard Manure of Charcol depends upon the amount of herbicides in the soil. Be careful in the determination of the amount of herbicide in soil or micro/macro flora.
I’m Dr Qaiser Maqsood (PhD), a dedicated researcher and expert in Biological Sciences, Gardening, Bio-Diversity, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences. I’m much concerned about Environmental Pollution, Climate Change, Plantation, Gardening, and Global Warming. My passion is to explore innovative solutions in all these fields.
Be aware that we have ONLY ONE EARTH. Protect it!!