Discover 15 Types of Coconut Trees | Facts and their Importance?
Coconut trees are scientifically known as “Cocos nucifera”. Types of coconut trees are famous for their versatility, diversity, and abundance. The name “coconut” comes from Portuguese where coco means head or skull, and nut is a fruit with a hard shell. Coconut is a national tree of the Maldives.
5 Prominent Facts about Coconuts
This succulent and fleshy fruit has some mysteries. Let’s try to explore them.
- Coconut trees can grow up to 100 feet
- Coconut contains 94% water
- It can produce 60 (dwarf) to 180 (tall) fruits in a single harvest.
- Coconut oil contains MCT (medium chain triglycerides) which are healthy and easy to digest.
- The total production of coconuts exceeds 60 million tonnes in a year. Indonesia, the Philippines, and India are the largest producers.
What are coconut bras?
Coconut bras are part of traditional costumes. It is believed that this tradition started in Hawaii islands and is now common in all the Pacific islands. It is used at special occasions e.g. weddings and traditional dance parties.
How Many Different Types of Coconut Trees are there?
Are you curious to know the different types of coconuts? There are various types of coconut trees depending upon their physical or edaphic features. All of them possess unique characteristics. All this is what we will find in this article. Let’s explore some of these remarkable coconut tree varieties:
1. Indonesia Coconut
With its extensive coastline, Indonesia is home to a diverse range of coconut tree varieties. These types of coconut trees make Indonesia rank first in coconut production. These coconuts are widely used in Indonesian cuisine, as well as for their versatile oil and fiber.

2. King Coconut
Fit for royalty, the King Coconut tree graces the landscapes of Sri Lanka and India. It is called the “tree of life” in Sri Lanka, as the tree plays a pivotal role in the country’s culture and economy. Its stature is remarkable and can grow up to 20 meters. It bears dense fruits (20 fruits per branch) ranging from 20-30 cm in diameter. Yellowish fruit with flavored water can refresh and hydrate you.
Its juice and flesh contain amino acids, vitamins, phosphate, potassium, and some active enzymes. All these biomolecules are associated with metabolism and are thus nutritious for humans.

3. East Coast Tall Coconuts
These are medium-sized trees. They are highly productive with 70 -80 coconuts per year. Their produce is high in oil content (more than 65%). They can withstand hot weather conditions.
Flourishing along the eastern coastlines, the East Coast Tall coconut tree exhibits remarkable adaptability to this climate. They become productive at the age of 7 and can bear up to 70 nuts per plant. The nut juice is rich in oil content (65%). It is moderately tolerant to disease and pests due to its tall size. Bugs and mites do not disturb its growth.

4. West Coast Tall Coconut
Thriving along the western coastlines, this tall coconut tree variety is highly diverse. It can grow in a wide range of climate and soil conditions. They can be productive in just 7 to 8 years.
Their fruit size is perfect. They bear 80 to 90 fruits per plant. It is known for its high yield and resilience against strong winds and saline soil and water. It produces coconuts rich in oil content suitable for cosmetic use.

5. Panama Tall Coconut
Native to Panama and the Pacific, the Panama Tall coconut tree forms an umbrella-shaped canopy. They exhibit exceptional resistance to harsh climates and pests and diseases.
Their high resistance to lower temperatures and umbrella shape makes them a good choice for gardeners. Moreover, their resistance to wind and temperature makes them tall enough that they can go up to 90 feet (25 – 30 m).

6. Macapuno Coconut/Kopyor Coconut
Hailing from the Philippines, the Macapuno coconut tree bears unique mutant coconuts with thick, soft, and jelly-like flesh. Their endospermic part makes them so and is edible, often used in desserts.
As the endospermic part grows abruptly, the liquid content is almost zero in these types of Coconut Trees. This made is less favorable and only used for dishes and desserts. They also contain oil and protein contents. Moreover, their commercial importance makes them a bit costly.

7. Mayan Coconut
This may be called a hybrid between the Malayan short coconut tree and Panama Tall coconut varieties. This variant of the Coconut tree was developed in the 1990s. At that time, yellowing disease was destroying all types of coconut and thus, the Maypan variant was developed.
: It can grow up to 60 feet (18-20 m) in height. This is known as a “Hybrid” variety of Coconut and is famous for its high productivity and resistance to yellowing disease. These are types of coconut trees in Jamaica.
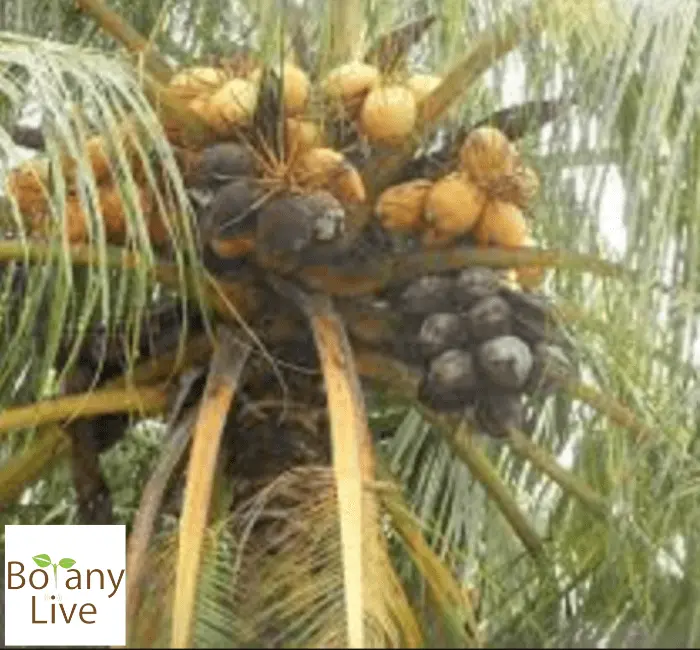

8. VHC1 Coconut
As the name shows, the variant of coconut trees is a hybrid. This is a cross combination of east coast tall and Malayan Dwarf. This combination resulted in a highly fertile and productive type of coconut.
VHC1 can produce fruits at the age of 4 years, this least time to get productivity. This mid heighted type of coconut tree may give up to 100 fruits. It has become a valuable asset for the local coconut industry.

9. Tiptur Tall
Originating from Tiptur in India, the Tiptur Tall coconut tree is renowned for its leathery fronds. Fronds are the leaves – leaflets of coconuts and other palm trees. It can be productive in 7-8 years and is moderately productive in terms of the number of fruits.
It requires less maintenance and thus is liked for home décor and l landscape.

10. Cameron Red Dwarf
This is the most vibrant variety because of its color. The color of the fruit is red to yellow-orange and is pear-shaped. One of the most significant uses of this variety of coconuts is its prime place in ornamentals.
11. Green Dwarf
The Green Dwarf coconut tree is prized for its deep green fronds. it’s compact, low statured, and attains early maturity (only 3 – 4 years). Moreover, similar to other dwarf types of coconut trees, these miniature coconut trees are also susceptible to diseases.
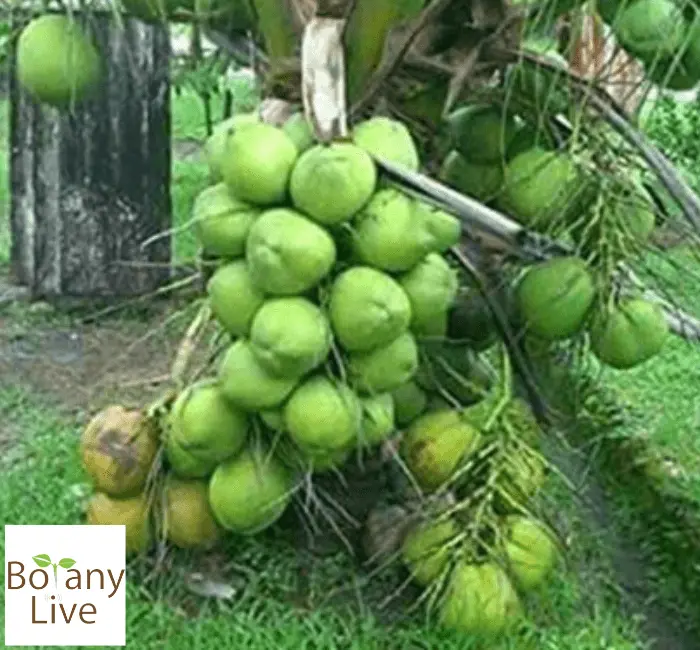

12. Chowghat Dwarf Orange
They are just 15 to 20 feet in height. They are one of the early producers and can produce at the age of 3 to 3.5 years. You can easily pick their 60-65 fruits yearly. However, the flesh content of this dwarf is the least in all types of coconut trees.
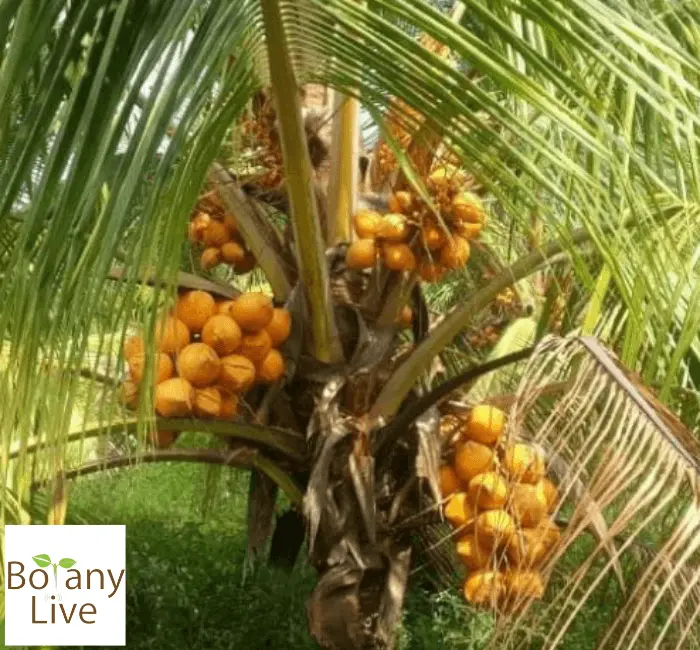

13. Golden Malay
This type is native to Malay and Indonesia. The fruit shows its golden hue when ripens. The Golden Malay coconut tree is cherished for its juicy and refreshing water. They love tropical climates and soil with good organic matter. Organic matter-rich soil and tropical climate help it in attaining heights up to 12 meters.
This type is famous for producing fruits at an early stage. It gives high-quality drinking water and flesh – used for cooking.
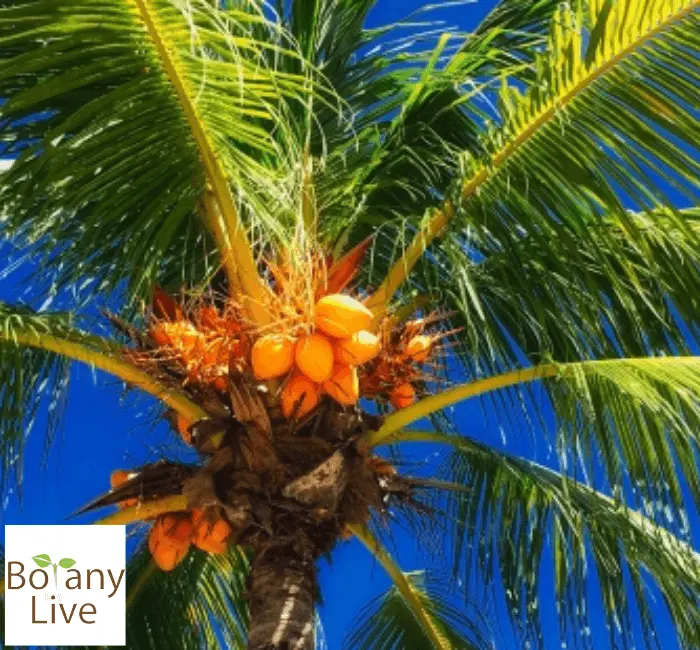

14. Malayan Yellow Dwarf Coconuts
This dwarf coconut variety, with its vibrant yellow color, is highly prized for its sweet and aromatic water. It’s commonly found in tropical areas of Southeast Asia like Bennettitales and their affinity groups. It is best suited in soils enriched in organic matter.
The fruit is greenish when unripe. However, at maturity, the fruit and stem, leaves turn pale yellow. Short height and yellowish shade earn its name as “Malayan Yellow Dwarf”. Yellowish fruit (700-800 grams in weight) is a favorite among locals and tourists alike. They are perfectly round Jamaican Coconuts. Yellow Coconut stands out with its bright yellow husk covering the sweet flesh. It offers a delightful blend of sweetness and nutrition and is refreshing coconut water.
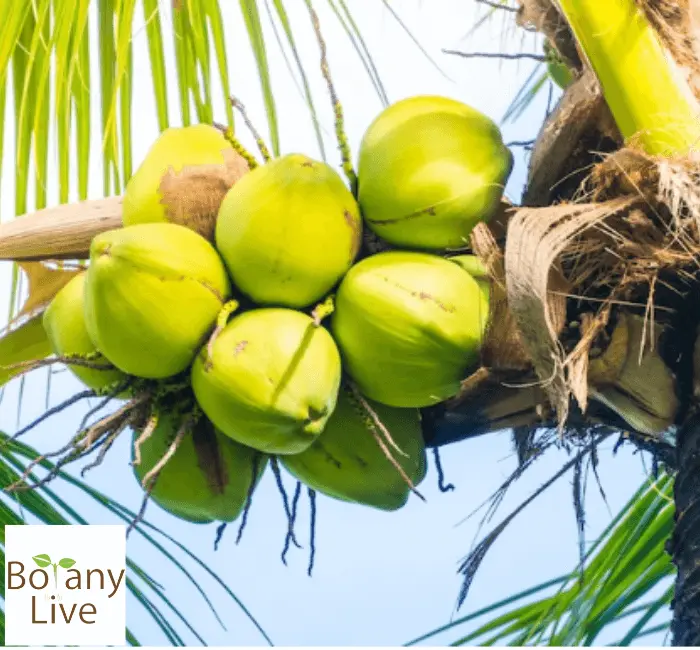

15. Fiji Dwarf
Originating from the enchanting islands of Fiji and Florida. This coconut species emerge as a leading variety of Coconut after the 1980s. This shows that it is quite resistant to disease and pests.
People can easily harvest its fruit without any ladder, standing on the ground. However, the tree can increase in height at the rate of 1 meter per annum. Its short stature makes it perfect for ornamental uses. The fruit is compact, smooth texture, has a tough nut, and is mild in flavor. It is highly adaptable and can flourish in diverse environments.

What is the Importance of Coconut Trees?
We have learned a lot about the coconut tree, its fruits, fruit parts, and types of coconut trees. Now, we are here to look into some of the aspects showing the importance of coconuts.
- Coconut milk is a healthy fresher drink. It relieves in dehydrations as it contains 95% water content.
- Coconut oil mixed with tea tree oil serve as a skin care treatment. It helps in treating water warts and irritation. Mix these two in a ratio of 10 drops of tea tree oil and 2 tablespoons of coconut oil is
- Coconut oil is good for hair growth and protection. Mixed with tea extract, it serves the purpose in a better way. It also serves its purpose to kill and repel lice.
- Coconut tree costumes and coconut bras are common in different parts of the earth on special occasions.
- Coconut lime body wash is a commercial product and is nutritive for the skin, especially the face and hands.
- Coconut oil mixed with sugar makes a perfect sugar scrub for the skin. It is used as a usual skin massage.
- Coconut juice help to control blood sugar level as it is high in fibers. It also helps in crabs and hunger pangs.
- Husk removed from the seed is fibrous. It is used in making threads and ropes.
- It leaves are called fronds. These fronds serve as a broom well and help in domestic cleaning.
Importance of Coconut Water and Raw meat? A Comparison Table
FAQs
I’m Dr Qaiser Maqsood (PhD), a dedicated researcher and expert in Biological Sciences, Gardening, Bio-Diversity, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences. I’m much concerned about Environmental Pollution, Climate Change, Plantation, Gardening, and Global Warming. My passion is to explore innovative solutions in all these fields.
Be aware that we have ONLY ONE EARTH. Protect it!!